type
status
date
slug
summary
tags
category
icon
password
kube-jenkins示意图1. scripted pipline 常规1.1 Scripted Pipeline 基础结构说明:1.2 Scripted Pipeline 语法示例:1.3 Jenkins slave pod pipeline简单样本1.3.1 credentialsId配置1.3.2 deploy $env stuff 的实现1.3.3 maven打包-插件1.3.4 maven打包-自建jnlp镜像1.3.5 maven打包-一个pod内多个container1.4 Jenkins slave pod pipeline复杂样本2. scripted pipline 参数2.1 node模块内使用parameters参数2.2 node模块外使用parameters参数2.3 parameters模块更多参考用法2.4 直接使用def3. scripted pipline 引号4. scripted pipline 使用EOF
kube-jenkins示意图

1. scripted pipline 常规
描述: Scripted Pipeline 是基于 groovy 的一种
DSL 语言相比于 Declarative pipeline,它为jenkins用户提供了更巨大的灵活性和可扩展性。如无特殊说明,后续pipeline全部采用scripted pipline。
1.1 Scripted Pipeline 基础结构说明:
- Node:节点,一个 Node 就是一个 Jenkins 节点,Master 或者 Agent,是执行 Step 的具体运行环境,比如我们之前动态运行的 Jenkins Slave 就是一个 Node 节点
- Stage:阶段,一个 Pipeline 可以划分为若干个 Stage,每个 Stage 代表一组操作,比如:Build、Test、Deploy,Stage 是一个逻辑分组的概念,可以跨多个 Node
1.2 Scripted Pipeline 语法示例:
// Jenkinsfile (Scripted Pipeline) // #结构1 node { // @变量定义 def mvnHome // #结构2 stage('Preparation') { // # 结构3 - 它就是 Step 基本操作单元 echo "Scripted Pipeline" } }
Tips : 注释(Comments)和Java一样,
支持单行(使用//)、多行(/* */)和文档注释(使用/** */)。1.3 Jenkins slave pod pipeline简单样本
node('haimaxy-jnlp') { stage('Clone') { echo "1.Clone Stage" /* stage("Git 远程仓库拉取"){ //使用鉴权credentialsId git url: "https://github.com/my-dlq/test.git", credentialsId: "git-global-credentials", branch: "master" } */ //branch默认是master,完整写法git branch: 'main', url:'https://github.com/naiveskill/devops.git' git url: "https://github.com/cnych/jenkins-demo.git" // script调用groovy脚本 script { build_tag = sh(returnStdout: true, script: 'git rev-parse --short HEAD').trim() } } stage('Test') { echo "2.Test Stage" } stage('Build') { echo "3.Build Docker Image Stage" sh "docker build -t cnych/jenkins-demo:${build_tag} ." } stage('Push') { echo "4.Push Docker Image Stage" //使用鉴权credentialsId withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: 'dockerHub', passwordVariable: 'dockerHubPassword', usernameVariable: 'dockerHubUser')]) { sh "docker login -u ${dockerHubUser} -p ${dockerHubPassword}" sh "docker push cnych/jenkins-demo:${build_tag}" } } stage('Deploy') { echo "5. Deploy Stage" //input调出交互式 def userInput = input( id: 'userInput', message: 'Choose a deploy environment', parameters: [ [ $class: 'ChoiceParameterDefinition', choices: "Dev\nQA\nProd", name: 'Env' ] ] ) echo "This is a deploy step to ${userInput}" sh "sed -i 's/<BUILD_TAG>/${build_tag}/' k8s.yaml" //env.BRANCH_NAME是Jenkins自带env sh "sed -i 's/<BRANCH_NAME>/${env.BRANCH_NAME}/' k8s.yaml" if (userInput == "Dev") { // deploy dev stuff } else if (userInput == "QA"){ // deploy qa stuff } else { // deploy prod stuff } sh "kubectl apply -f k8s.yaml" } }
样本解析的补充:
1.3.1 credentialsId配置
在首页点击 Credentials -> Stores scoped to Jenkins 下面的 Jenkins -> Global credentials (unrestricted) -> 左侧的 Add Credentials:添加一个 Username with password 类型的认证信息,如下:
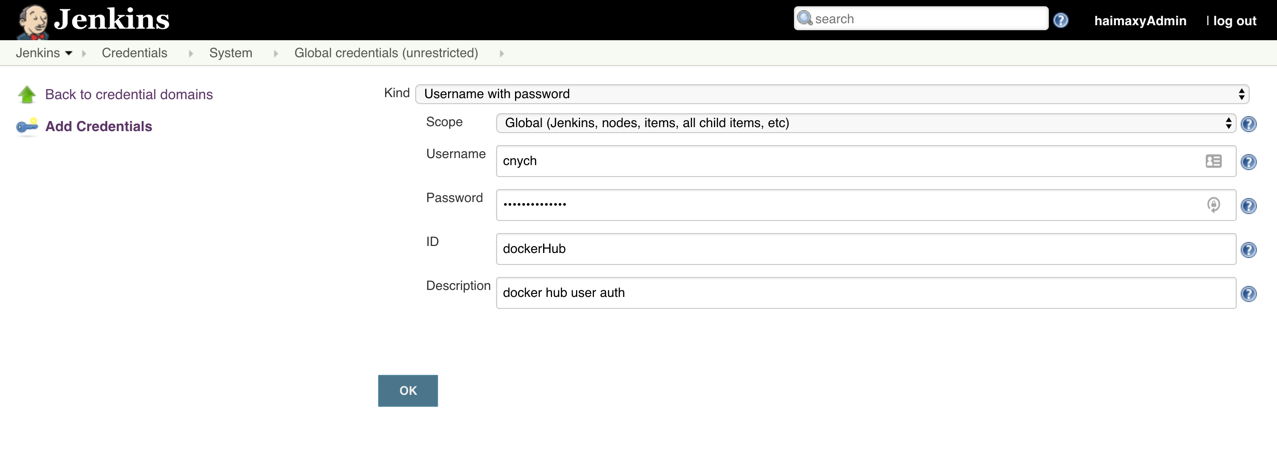
1.3.2 deploy $env stuff 的实现
- 可以把多个集群的context集中起来,一般默认放在
$Home/.kube,需要时use context。由于slave pod可能存在于每个节点,故每台节点的$Home/.kube要一致。
$Home/.kube 是配置 pod template时挂载的。
- 读取
Secret text,在pod创建~/.kube,解密Credentials生成context。这样只需要在凭据菜单配置多个集群的Credentials,不需要每个节点都配置~/.kube。more
注意:凭据设置界面,类型需要选择为“Secret text”
样例1:声明式pipeline,
K8S_CONFIG = credentials('jenkins-k8s-config') K8S_CONFIG = credentials('jenkins-k8s-config') sh "mkdir -p ~/.kube" sh "echo ${K8S_CONFIG} | base64 -d > ~/.kube/config"
样例2:scripted pipeline,
withCredentials string ,morenode { withCredentials([string(credentialsId: 'prod-k8s-config', variable: 'TOKEN')]) { sh ''' set +x echo "Token: $TOKEN" ''' } }
- 参考此文第四部分secret设置
1.3.3 maven打包-插件
可以看到stage部分不涉及maven build,如果需要使用maven,可以先安装插件,在加入stage。more
既然是插件就涉及到安装目录,因为是pod形式,slave pod能否读取到master pod插件的安装目录?未验证。可以考虑映射到NFS,或者每台节点都有对应的插件目录,pod template用hostpath挂载。
node{ stage('get clone'){ //check CODE echo 'Checkout==========》》》' checkout([$class: 'GitSCM', branches: [[name: '*/master']], doGenerateSubmoduleConfigurations: false, extensions: [], submoduleCfg: [], userRemoteConfigs: [[url: 'https://source.enncloud.cn/qinzhao/spring-boot-demo.git']]]) } //定义mvn环境 //插件里定义的maven变量名称为maven3.5.3,接下来在Jenkinsfile中使用tool获取变量值 def mvnHome = tool 'maven3.5.3' env.PATH = "${mvnHome}/bin:${env.PATH}" stage('mvn test'){ //mvn 测试 sh "mvn test" } stage('mvn build'){ //mvn构建 sh "mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip=true" } stage('deploy'){ //执行部署脚本 echo "deploy ......" } }
The def keyword in Groovy is the quickest way to define a new variable (with no specific type). In the sample syntax discussed above, a variable is defined by the following expression:
def mvnHome = tool 'M3'
This ensures that M3 is installed somewhere accessible to Jenkins and assigns the return value of the step (an installation path) to the mvnHome variable.

1.3.4 maven打包-自建jnlp镜像
Jenkins是master/agent的架构。而master与agent之间通信方法有两种:
- 通过JNLP协议:需要启动JNLP客户端主动连接master。这是Kubernetes插件使用的方式。
- 通过SSH协议:master使用SSH主动连接agent机器。
Kubernetes插件的具体的做法就是连接到Kubernetes集群,然后启动一个Pod。Pod中包含一个JNLP客户端,容器名约定为:jnlp。jnlp 会主动连接Jenkins master。所以,当你发现Jenkins任务的日志中,一直在等待jnlp连接时,我们可以这样查问题:
- 查看相应的Pod是否存活。
- jnlp 容器连接不上master:大概率是配置不对。
pod template的containerTemplate的image尽量写详细,即$registy/$image-name:$version,如果简写,插件会拉取官方仓库的镜像,非常慢或者拉取失败。
关于image简写的另一个问题:
我的容器运行时是contained,我简写手动拉取docker镜像时总是失败,比如命令是
crictl --debug pull kubectl ,则一直失败,报错如下。但是换完整的image则正常,如crictl --debug pull docker.io/bitnami/kubectl:latestcrictl --debug pull kubectl DEBU[0000] get image connection DEBU[0000] PullImageRequest: &PullImageRequest{Image:&ImageSpec{Image:kubectl,Annotations:map[string]string{},},Auth:nil,SandboxConfig:nil,} E0422 13:17:37.290471 83274 remote_image.go:171] "PullImage from image service failed" err="rpc error: code = Unknown desc = failed to pull and unpack image \"docker.io/library/kubectl:latest\": failed to resolve reference \"docker.io/library/kubectl:latest\": pull access denied, repository does not exist or may require authorization: server message: insufficient_scope: authorization failed" image="kubectl" FATA[0002] pulling image: rpc error: code = Unknown desc = failed to pull and unpack image "docker.io/library/kubectl:latest": failed to resolve reference "docker.io/library/kubectl:latest": pull access denied, repository does not exist or may require authorization: server message: insufficient_scope: authorization failedm'lm'lm'l
crictl --debug pull docker.io/bitnami/kubectl:latest DEBU[0000] get image connection DEBU[0000] PullImageRequest: &PullImageRequest{Image:&ImageSpec{Image:docker.io/bitnami/kubectl:latest,Annotations:map[string]string{},},Auth:nil,SandboxConfig:nil,} DEBU[0017] PullImageResponse: &PullImageResponse{ImageRef:sha256:1fb61441fdb4b8e3d637219d960edea85f52319a0d76a2346da0dfacc8f1ed8f,} Image is up to date for sha256:1fb61441fdb4b8e3d637219d960edea85f52319a0d76a2346da0dfacc8f1ed8f
为什么即使我们不显示配置jnlp的容器,slave pod也可以run呢?这是因为Jenkins kubernates插件在真正创建pod前,为我们加入了默认的jnlp的container。
默认的jnlp拉取镜像时可能存在网络问题,而且功能单一,故更多人会选择定制镜像,然后显示指定。自定义镜像因为把maven等工具写死了,故欠缺灵活性。显示指定有两种方式:
- 插件配置

- pipeline配置
def label = "jenkins-slave" podTemplate(label: label, containers: [ containerTemplate(name: 'kubectl', image: 'boer0924/jenkins-slave:1.18.3', command: 'cat', ttyEnabled: true)], serviceAccount: 'jenkins', volumes: [ hostPathVolume(mountPath: '/root/.m2', hostPath: '/var/lib/cache/.m2'), hostPathVolume(mountPath: '/var/run/docker.sock', hostPath: '/var/run/docker.sock'), hostPathVolume(mountPath: '/var/lib/docker', hostPath: '/var/lib/docker') ]) { node(label) { //depoly } }
1.3.5 maven打包-一个pod内多个container
pod内可以存在多个container,故可以考虑每个工具一个container,合并成slave pod。这样做灵活性增强,研发可以根据需求指定不同的工具。多个container是否存在目录共享的问题?即假如maven容器创建了app.jar,那docker容器的docker命令是否可以感知到这个jar?很多博文未提及这点,或许因为现在我还不知道某些细节。当然,sidecar模式共享一个emptyDIR肯定可以解决文件共享的问题。我杞人忧天了,官方已经解决了这个问题😢。
多个container时,即使不显示指定inbound-agent镜像,执行任务时也会自动下载。故建议先提前下载到本地仓库,避免网络问题。
多container共享目录的疑问(已解决,见下一条toggle list)
此文或许可以解答我的问题:
dockerfile的
ADD target/*.jar app.jar 使用了相对路径,读取pom时pom = readMavenPom file: './pom.xml’ 也使用了相对路径,而在pipeline中上一步是maven容器在$jenkinshome 输出了前面两个文件,下一步docker容器直接使用相对路径引用jar和pom.xml,说明多个容器都在$jenkinshome 执行任务。日志样本:
[INFO] --- spring-boot-maven-plugin:2.1.4.RELEASE:repackage (repackage) @ springboot-helloword --- [INFO] Replacing main artifact with repackaged archive [INFO] [INFO] --- maven-install-plugin:2.5.2:install (default-install) @ springboot-helloword --- [INFO] Installing /home/jenkins/workspace/k8s-pipeline/target/springboot-helloword-0.0.1.jar to /root/.m2/repository/club/mydlq/springboot-helloword/0.0.1/springboot-helloword-0.0.1.jar [INFO] Installing /home/jenkins/workspace/k8s-pipeline/pom.xml to /root/.m2/repository/club/mydlq/springboot-helloword/0.0.1/springboot-helloword-0.0.1.pom [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] BUILD SUCCESS
pipeline样本:
stage('Maven阶段'){ echo "Maven 阶段" container('maven') { //这里引用上面设置的全局的 settings.xml 文件,根据其ID将其引入并创建该文件 configFileProvider([configFile(fileId: "75884c5a-4ec2-4dc0-8d87-58b6b1636f8a", targetLocation: "settings.xml")]){ sh "mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip=true --settings settings.xml" } } } stage('Docker阶段'){ echo "Docker 阶段" container('docker') { // 读取pom参数 echo "读取 pom.xml 参数" //'./pom.xml'是相对目录,maven容器输出的是/home/jenkins/workspace/k8s-pipeline/pom.xml pom = readMavenPom file: './pom.xml' } }
多container共享目录的解答(验证)
kubernetes 插件就是用sidecar模式共享一个emptyDIR解决的此问题,即所有pod的$workdir都挂载共同的emptyDIR。验证很简单:1.构造一个多容器pipeline,2.观察日志里生成的slave deployment spec。
- 多容器pipeline
def label = "jenkins-slave-${UUID.randomUUID().toString()}" podTemplate(label: label, cloud: 'kubernetes', containers: [ containerTemplate(name: 'maven', image: 'docker.io/library/maven:latest', ttyEnabled: true, command: 'cat'), containerTemplate(name: 'kubectl', image: 'docker.io/bitnami/kubectl:latest', command: 'cat', ttyEnabled: true)], volumes: [ persistentVolumeClaim(mountPath: '/root/.m2', claimName: 'jenkins-m2'), persistentVolumeClaim(mountPath: '/home/jenkins/agent/workspace', claimName: 'jenkins-agent'), secretVolume(secretName: 'jenkins-k8s-cfg', mountPath: '/home/jenkins/agent/.kube/config')] ){ node(label){ stage('build'){ git branch: 'master', url: 'https://github.com/my-dlq/springboot-helloworld.git' container('maven') { stage('Build a Maven project') { sh 'mvn clean package -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -DskipTests=true' } } } stage('kubectl'){ container('kubectl') { sh 'kubectl get pod -A' } } } }
- 日志输出含spec的部分
spec: containers: - command: - "cat" image: "docker.io/library/maven:latest" imagePullPolicy: "IfNotPresent" name: "maven" resources: {} tty: true volumeMounts: - mountPath: "/home/jenkins/agent/.kube/config" name: "volume-2" readOnly: false - mountPath: "/root/.m2" name: "volume-0" readOnly: false - mountPath: "/home/jenkins/agent/workspace" name: "volume-1" readOnly: false #挂载了emptyDIR "workspace-volume" - mountPath: "/home/jenkins/agent" name: "workspace-volume" readOnly: false - command: - "cat" image: "docker.io/bitnami/kubectl:latest" imagePullPolicy: "IfNotPresent" name: "kubectl" resources: {} tty: true volumeMounts: - mountPath: "/home/jenkins/agent/.kube/config" name: "volume-2" readOnly: false - mountPath: "/root/.m2" name: "volume-0" readOnly: false - mountPath: "/home/jenkins/agent/workspace" name: "volume-1" readOnly: false #挂载了emptyDIR "workspace-volume" - mountPath: "/home/jenkins/agent" name: "workspace-volume" readOnly: false - env: - name: "JENKINS_SECRET" value: "********" - name: "JENKINS_TUNNEL" value: "10.110.43.229:50000" - name: "JENKINS_AGENT_NAME" value: "jenkins-slave-83079b52-d127-4e36-9cc7-649b56b60209-fvjqh-1fnh3" - name: "JENKINS_NAME" value: "jenkins-slave-83079b52-d127-4e36-9cc7-649b56b60209-fvjqh-1fnh3" - name: "JENKINS_AGENT_WORKDIR" value: "/home/jenkins/agent" - name: "JENKINS_URL" value: "http://10.110.43.229:8080/" image: "jenkins/inbound-agent:3107.v665000b_51092-5" name: "jnlp" resources: requests: memory: "256Mi" cpu: "100m" volumeMounts: - mountPath: "/home/jenkins/agent/.kube/config" name: "volume-2" readOnly: false - mountPath: "/root/.m2" name: "volume-0" readOnly: false - mountPath: "/home/jenkins/agent/workspace" name: "volume-1" readOnly: false #挂载了emptyDIR "workspace-volume" - mountPath: "/home/jenkins/agent" name: "workspace-volume" readOnly: false nodeSelector: kubernetes.io/os: "linux" restartPolicy: "Never" volumes: - name: "volume-0" persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: "jenkins-m2" readOnly: false - name: "volume-2" secret: secretName: "jenkins-k8s-cfg" - name: "volume-1" persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: "jenkins-agent" readOnly: false - emptyDir: medium: "" name: "workspace-volume"
podTemplate(containers: [ containerTemplate(name: 'maven', image: 'maven:3.8.1-jdk-8', command: 'sleep', args: '99d'), containerTemplate(name: 'golang', image: 'golang:1.16.5', command: 'sleep', args: '99d') ]) { node(POD_LABEL) { stage('Get a Maven project') { git 'https://github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-plugin.git' container('maven') { stage('Build a Maven project') { sh 'mvn -B -ntp clean install' } } } stage('Get a Golang project') { git url: 'https://github.com/hashicorp/terraform.git', branch: 'main' container('golang') { stage('Build a Go project') { sh ''' mkdir -p /go/src/github.com/hashicorp ln -s `pwd` /go/src/github.com/hashicorp/terraform cd /go/src/github.com/hashicorp/terraform && make ''' } } } } }
1.4 Jenkins slave pod pipeline复杂样本
参数解释:
- 定义agent label是为在k8s中调度job的pod名字
- 定义parameters来选择需要部署的环境。
- Jenkinsfile的两个全局变量:env/params。 设置env变量:
env.KEY = value,使用env变量:${KEY}
- username&password凭证的使用:
registryCre = credentials('registry')[_USR/_PSW],获取username:${registryCre_USR},获取passowrd:${registryCre_PSW}
- 使用short commit_id作为image_tag 和
kubernetes.io/change-cause, 以保证镜像唯一,和可以回退到指定版本。
- sed动态修改k8s资源定义文件manifests/k8s.yaml:
- : 便于指定版本回退
- : 指定版本
- : 不同环境不同域名
def label = "jenkins-slave" properties([ parameters([ choice(name: 'ENV', choices: ['test', 'pre', 'prod'], description: '选择部署环境?') ]) ]) podTemplate(label: label, containers: [ containerTemplate(name: 'maven', image: 'maven:3.6.3-jdk-8', command: 'cat', ttyEnabled: true), containerTemplate(name: 'docker', image: 'docker:19.03.8', command: 'cat', ttyEnabled: true), containerTemplate(name: 'kubectl', image: 'boer0924/kubectl:1.18.3', command: 'cat', ttyEnabled: true)], serviceAccount: 'jenkins', volumes: [ hostPathVolume(mountPath: '/root/.m2', hostPath: '/var/lib/cache/.m2'), hostPathVolume(mountPath: '/var/run/docker.sock', hostPath: '/var/run/docker.sock'), hostPathVolume(mountPath: '/var/lib/docker', hostPath: '/var/lib/docker') ]) { node(label) { if ("${params.ENV}" == 'test') { env.NAMESPACE = 'devops' env.INGRESS = 'test' } if ("${params.ENV}" == 'pre') { env.NAMESPACE = 'pre' env.INGRESS = 'pre' } if ("${params.ENV}" == 'prod') { env.NAMESPACE = 'prod' env.INGRESS = 'prod' } def myRepo = checkout scm def gitCommit = myRepo.GIT_COMMIT def gitBranch = myRepo.GIT_BRANCH def imageTag = sh(script: "git rev-parse --short HEAD", returnStdout: true).trim() def changeCause = sh(script: "git log --oneline -1 HEAD", returnStdout: true).trim() def dockerRegistryUrl = "registry.boer.xyz" def imageEndpoint = "public/spring-produce" def image = "${dockerRegistryUrl}/${imageEndpoint}" stage('单元测试') { echo "1.测试阶段" } stage('代码编译打包') { try { container('maven') { echo "2. 代码编译打包阶段" sh "mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true" } } catch (exc) { println "构建失败 - ${currentBuild.fullDisplayName}" throw(exc) } } stage('构建 Docker 镜像') { withCredentials([[$class: 'UsernamePasswordMultiBinding', credentialsId: 'dockerhub', usernameVariable: 'DOCKER_HUB_USER', passwordVariable: 'DOCKER_HUB_PASSWORD']]) { container('docker') { echo "3. 构建 Docker 镜像阶段" sh """ docker login ${dockerRegistryUrl} -u ${DOCKER_HUB_USER} -p ${DOCKER_HUB_PASSWORD} docker build -t ${image}:${imageTag} . docker push ${image}:${imageTag} """ } } } stage('运行 Kubectl') { withCredentials([file(credentialsId: 'kubeconfig', variable: 'KUBECONFIG')]) { container('kubectl') { sh "mkdir -p ~/.kube && cp ${KUBECONFIG} ~/.kube/config" echo "查看当前目录" sh """ sed -i "s|<CHANGE_CAUSE>|${changeCause}|g" manifests/k8s.yaml sed -i "s|<IMAGE>|${image}|g" manifests/k8s.yaml sed -i "s|<IMAGE_TAG>|${imageTag}|g" manifests/k8s.yaml sed -i "s|<INGRESS>|${INGRESS}|g" manifests/k8s.yaml kubectl apply -f manifests/k8s.yaml --namespace ${NAMESPACE} """ } } } stage('快速回滚?') { withCredentials([file(credentialsId: 'kubeconfig', variable: 'KUBECONFIG')]) { container('kubectl') { sh "mkdir -p ~/.kube && cp ${KUBECONFIG} ~/.kube/config" def userInput = input( id: 'userInput', message: '是否需要快速回滚?', parameters: [ [ $class: 'ChoiceParameterDefinition', choices: "N\nY", name: '回滚?' ] ] ) if (userInput == "Y") { sh "kubectl rollout undo deployment produce-deployment -n ${NAMESPACE}" } } } } } }
版本回退
- 1.根据
${COMMIT_ID}找出REVISION(自动)
- 2.根据
commit_msg找出REVISION(人工)
$ kubectl -n ${NAMESPACE} rollout history deployment consume-deployment deployment.apps/consume-deployment REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE 1 a03d0eb optimize change-cause msg 2 73f5a5c resource quota 3 2772a88 resource quota up 4 254b592 plus probe time 5 87989d8 更新配置文件 # 1.根据${COMMIT_ID}找出REVISION(自动) 2.根据commit_msg找出REVISION(人工) $ kubectl -n ${NAMESPACE} rollout undo deployment consume-deployment --to-revision=$(kubectl -n ${NAMESPACE} rollout history deployment consume-deployment | grep ${COMMIT_ID} | awk '{print $1}') $ kubectl -n ${NAMESPACE} rollout status deployment consume-deployment
2. scripted pipline 参数
2.1 node模块内使用parameters参数
引用parameters模块的参数时,
params. 可以省略node(){ properties([ parameters([ string(defaultValue: 'world', name: 'Name',description: "this is sth") ]) ]) sh "hello ${Name}" //sh "hello ${params.Name}" }
- 拓展:使用自定义env
node{ withEnv(['FName=Naive','LName=skill']) { stage('Build') { sh 'echo $FName $LName' } } }
2.2 node模块外使用parameters参数
properties( [ parameters([ string(defaultValue: '/data', name: 'Directory'), string(defaultValue: 'Dev', name: 'DEPLOY_ENV') ]) ] ) node { // params.DEPLOY_ENV ... }
2.3 parameters模块更多参考用法
properties( parameters ([ string(name: 'PERSON', defaultValue: 'Mr Jenkins', description: 'Who should I say hello to?'), text(name: 'BIOGRAPHY', defaultValue: '', description: 'Enter some information about the person'), booleanParam(name: 'TOGGLE', defaultValue: true, description: 'Toggle this value'), choice(name: 'CHOICE', choices: ['One', 'Two', 'Three'], description: 'Pick something'), password(name: 'PASSWORD', defaultValue: 'SECRET', description: 'Enter a password') ]) ])
2.4 直接使用def
node(){ def Name = 'world' sh "hello ${Name}" }
3. scripted pipline 引号
- 支持单引号、双引号。双引号支持插值(变量),单引号不支持。
- 支持三引号。三引号分为三单引号和三双引号。它们都支持换行,区别在于只有三双引号支持插值(变量)。
应用场景举例:需要用sh执行多条shell命令,第一步需要设置alias,后面引用这个alias。多行挤在一行可读性查,可以用三单引号。
As you know each sh command runs in it's own shell. It has same location as agent/workspace, but since it's a new shell, environment variables, aliases, etc, can be lost. So combine the lines into a single sh
stage('kubectl'){ container('kubectl') { sh ''' alias k="kubectl --kubeconfig=/home/jenkins/agent/.kube/config" k version k get pod -n demo ''' }
4. scripted pipline 使用EOF
sh模块使用多行可以用三单引号或者三双引号,如果sh的内容更复杂、嵌套多层,可以考虑配合EOF使用。不过groovy使用EOF有个不一样的点,通常
<<\-EOF (反斜杠是避免notion解析成箭头,实际没有),就可以让结尾的EOF忽略tab和空格,但是这里不行,需要配合.stripIndent() 使用参数时带上花括号,即${agrs}
stage('ssh2remote'){ sshagent(credentials: ['mysshkey']) { //第一步scp dist包到目的服务器,第二步,ssh登录到remote server,执行删除、解压等命令 //sh的三双引号是为了解析里面的变量 //.stripIndent() 是为了让第二个(尾部)EOF不用定格写,第一个EOF前的<<- 可以换成<< ,没区别 sh """ scp -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no ${tar}.tar.gz ${user}@${server1}:/tmp/ ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no ${user}@${server1} <<- EOF rm -f /tmp/{a.txt,b.txt} tar -zxvf /tmp/${tar}.tar.gz -C /tmp/ ls -lht /tmp EOF """.stripIndent() } }